Acetabular (Hip Socket) Fractures
What is an Acetabular Fracture (also known as a Hip Socket Fracture)?
An acetabular fracture is a break of the hip socket. These fractures usually result from high energy injuries such as car accidents in younger patients and most often from falls in the elderly patient. The hip socket can be broken into many pieces or just crack slightly depending on the quality of bone and the type of injury. These fractures are described according to where and how the bone breaks and they are classified into ten different types. Differentiation of these injuries can be complex and these injuries should be treated by an orthopedic trauma specialist.
What does the Acetabulum do?
The hip joint is a “ball-and-socket” joint that is made up of the acetabulum and the femoral head. The acetabulum is the socket or cup while the femoral head is the ball. The acetabulum is part of the pelvis. If the acetabulum is broken and the pieces are displaced, the hip can be unstable and dislocate or cause significant pain and disability. Like any joint, these surfaces are covered by cartilage. Smooth cartilage is important for a joint to glide smoothly. Irregularity of the cartilage can lead to arthritis.
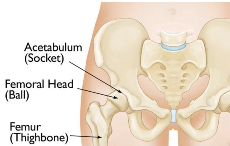
Reproduced with permission from OrthoInfo. © American Academy of Orthopaedic
Surgeons. https://orthoinfo.org/
Diagnosis and Examination
Many acetabular fractures occur from high energy injuries. Most patients are brought to a trauma center because these injuries often have associated head, chest or abdominal trauma. Physical examination is critical in the evaluation of these injuries. Important nerves and blood vessels run next to this bone and can be injured when it breaks. Diagnosis of an injury to some blood vessels requires urgent surgery. Associated hip dislocations can also result in damage to the sciatic nerve, which is the nerve that allows you to move your ankle and feel the bottom of your foot.
X-rays are used to evaluate the location and severity of the broken bone. This helps doctors and patients make an informed decision on treatment. Often 5 or more x-rays are taken to show the injury pattern. A CT (Computed Tomography) scan is often ordered to help plan treatment and surgery. These can create a 3-D image of the injury which gives doctors specific knowledge about the size and location of the broken bones.
Non-Surgical Treatment for Acetabular Fractures
Non-surgical treatment is recommended for very small stable fractures that are nondisplaced. It can also be recommended for elderly patients or those with serious medical problems like end stage renal disease or those at very high risk for complications.
If non-operative care is chosen, regular follow-up care for a physical exam and x-rays is important to ensure that the fracture stays in good position and heals appropriately. Cutting down or quitting smoking and tight blood sugar control if you are a diabetic is important for the healing process. One fall or continued lack of compliance with early walking against medical advice can cause bones to move and result in the need for surgery.
Depending on health and injury pattern this bone can take 3-4 months to heal without surgery. Physical therapy for hip and knee range of motion is started around 6 weeks once bone has healed enough to prevent displacement with motion.
Surgical Treatment for Hip Socket Fractures
Most acetabular fractures require surgery, and surgeons like to fix these fractures as soon as possible. However, due to the fact that many patients have other injuries, the surgery has to wait until patients are cleared for surgery by the general surgeons. Occasionally, surgery has to be delayed several days if patients are too sick or unstable from a medical standpoint for surgery.
Because the hip socket can break in many different ways, there are several types of surgery and surgical approaches that can be done to fix the injury. The surgeon will decide which is best for each injury pattern. In most cases, these are fixed with plates and screws. Most of these surgeries are done through very large incisions either placed over the hip and buttock or over the abdomen and pelvis. Many important nerves and blood vessels are around this joint and surgery is very serious. In some cases, the acetabulum is broken in so many pieces that it cannot be fixed with plates and screws, so a total hip replacement or arthroplasty is required. Surgery usually takes 1 to 3 hours. Most patients stay in the hospital for several days after surgery.
These are relatively rare injuries. It is important to choose your surgeon wisely. While in the hospital, it is your right as a patient to request the physician you think best to treat your injury. Extensive surgical experience can be helpful in achieving a good result and avoiding complications. Collectively, ROC orthopedic surgeons have performed more femur operations than any practice in Northern Nevada and take pride in outstanding surgical results. The ROC has 4 dedicated orthopedic trauma surgeons who work as a team to treat these difficult injuries.
After surgery, patients are not allowed to bear weight or walk for 6 to 10 weeks. You will be taught by physical therapy to use crutches or a walker before leaving the hospital. Your doctor may decide to put you on a blood thinner after surgery for 2-6 weeks depending on your risk factors.
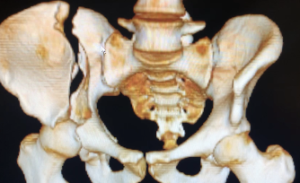
Preoperative CT scan of acetabular fracture
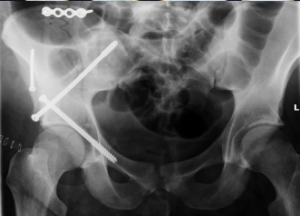
Postoperative x-ray of acetabular fracture repair.
Surgical Complications
Complications can occur with any surgery, no matter how small, and there is always a risk of infection. The risk is much greater for larger and more contaminated traumatic wounds. A dose of antibiotics given prior to surgery helps to make this risk as small as possible. There is always a risk of injury to blood vessels or nerves. This is reduced by having an experienced surgeon involved in your care. Patients with acetabular fractures are at risk of developing blood clots in the legs that can break off and go to the lungs, which can cause serious bleeding problems and even death. Non-compliance with blood thinning medication can have fatal consequences. It is always possible that the bone may not heal and additional surgery will be required. This is usually associated with patient non-compliance, diabetes, or use of nicotine like smoking and chewing tobacco. Any break into a joint can result in post-traumatic arthritis and pain. Sometimes this results in need for additional surgery such as total hip arthroplasty in the future. Another complication that can occur is heterotopic ossification, which is a condition where bone forms around the hip joint in the soft tissues or muscle where it should not be. This causes loss of motion, pain and stiffness, and sometimes surgical excision is required. Finally, the blood supply to the bone can be injured from the accident. It is not possible for the surgeon to tell at the time of the operation. This can cause the bone to die and collapse. This would be found on follow up x-rays in the office and could lead to severe arthritis requiring a total hip replacement.
Outcomes
Most people with acetabular fractures take about 4-6 months to heal. If anatomic alignment was achieved at surgery and no complications occur, patients are able to return to prior activities and function. By six weeks, patients are fairly comfortable. They cannot be released to full activities such as manual labor, skiing and motocross until about 6 months. Aggressive return to activity too early can result in re-fracture, hardware breakage or non-union, and in these cases revision surgery is required. Hips that become painful or develop arthritis can eventually require total hip replacement. If x-rays at 1 year after surgery show no signs of arthritis, patients are unlikely to require any additional surgery.
