Femoral Shaft Fractures
What is a Femoral Shaft Fracture?
A femoral shaft fracture is a break of the thigh bone between the hip and the knee. These fractures usually result from high energy injuries such as car accidents in younger patients and most often from falls in the elderly patient. The femur can be broken into many pieces or just crack slightly depending on the quality of bone and the type of injury. These fractures are described according to where and how the bone breaks.
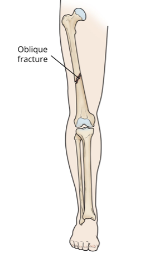
Illustration of femoral shaft bone.
Reproduced with permission from OrthoInfo. © American Academy of Orthopaedic
Surgeons. https://orthoinfo.org/
What does the Distal Femur do?
The femur is the biggest and strongest bone in the body. The femoral shaft connects the knee and hip joints. It provides stability and supports the entire body weight for walking, running and jumping.
Diagnosis for Femoral Shaft Fractures
Physical examination is critical in the evaluation of these injuries. Important nerves and blood vessels run next to this bone and can be injured when it breaks. Diagnosis of an injury to some blood vessels requires urgent surgery. The doctor will look for any open wounds over the injury as these usually require surgery. Often, the bone tries to poke out of the skin or “tent.” If this is not corrected, the skin can die or the bone can eventually cut the skin.
X-rays are used to evaluate the location and severity of the broken bone. This helps doctors and patients make an informed decision on treatment. Often 2 or more x-rays are taken to show the injury pattern. If the crack extend towards the hip or knee joint, a CT (Computed Tomography) scan is often ordered to help plan treatment and surgery. Sometimes an MRI is ordered for small fractures or to help diagnose stress fractures that do not show up on plain x-rays.
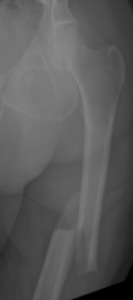
Preoperative x-ray of femoral shaft fracture.
Non-Surgical Femoral Shaft Fracture Treatment
Very few femoral shaft fractures in adults are treated without surgery. Most require surgery to heal correctly. Young children can be treated with braces or casts up to the age of five.
If non-operative care is chosen, regular follow-up care for a physical exam and x-rays is important to ensure that the fracture stays in good position and heals appropriately. Cutting down or quitting smoking and tight blood sugar control if you are a diabetic is important for the healing process. One fall or continued lack of compliance with casting, bracing or early walking against medical advice can cause bones to move and result in the need for surgery.
Depending on health and injury pattern this bone can take 3-4 months to heal without surgery. Physical therapy for hip and knee range of motion is started around 6 weeks once bone has healed enough to prevent displacement with motion.
Surgical Treatment for Femoral Shaft Fractures
Surgeons like to fix femoral shaft fractures as soon as possible. Occasionally surgery has to be delayed if patients are too sick or unstable from a medical standpoint for surgery
The femur can be fixed with metal plates and screws or intramedullary nails. The most common treatment is an intramedullary nail placed through a small incision at the hip or knee. This surgery has an extremely high success rate and often allows for immediate weight bearing. Plates and screws can be used but must be placed through larger incisions and don’t allow for immediate weight bearing. These are usually utilized in children with open growth plates or adults with total hip or knee replacements which make intramedullary nailing impossible. Surgery usually takes one to two hours. Most patients are admitted overnight.
In cases where there is severe injury to the muscles, nerves or arteries or there is significant contamination with dirt, rocks or grass from the injury, some patient require external fixation prior to definitive surgical treatment. This is an operation where metal pins are placed into the bone through small cuts and connected to bars to give some stability to the bone. After secondary operations to clean the wound or recovery of skin injuries, the external fixator can be removed and plates and intramedullary nails or plates and screws can be placed.
It is important to choose your surgeon wisely. Extensive surgical experience can be helpful in achieving a good result and avoiding complications. Collectively, ROC orthopedic surgeons have performed more femur operations than any practice in Northern Nevada and take pride in outstanding surgical results.
After surgery, patients are often allowed to bear weight immediately. Patients will need to use a walker or crutches for the first 6 weeks. Gentle motion of the hip and knee is begun early to prevent stiffness. Gradually this motion is increased and physical therapy is begun around 6 weeks after surgery if the patient has residual knee or ankle stiffness. Your doctor may decide to put you on a blood thinner after surgery for 2-6 weeks depending on your risk factors.
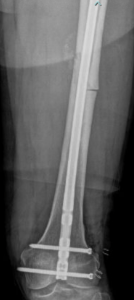
Postoperative x-ray of femoral shaft fracture repair with an intramedullary nail.
Surgical Complications
Complications can occur with any surgery, no matter how small. There is always a risk of infection. The risk is much bigger for larger and more contaminated traumatic wounds. A dose of antibiotics given prior to surgery helps to make this risk as small as possible. There is always a risk of injury to blood vessels or nerves. This is reduced by having an experienced surgeon involved in your care. Patients with femur fractures are at risk of developing blood clots in the legs that can break off and go to the lungs. This can cause serious bleeding problems and even death. Noncompliance with blood thinning medication can have fatal consequences. It is always possible that the bone may not heal and additional surgery will be required. This is usually associated with patient noncompliance, diabetes, or use of nicotine like smoking and chewing tobacco.
Outcomes
Most people with femoral shaft fractures do very well and return to prior activities and function. By six weeks, patients are extremely comfortable. They cannot be released to full activities such as manual labor, skiing and motocross until about three months. Aggressive return to activity too early can result in re-fracture, hardware breakage or nonunion. In these cases revision surgery is required. Sometimes metal hardware can irritate muscles and tendons. This can be removed one year after surgery.
Why Choose ROC for Your Femoral Shaft Fracture Surgery?
It is important to choose your surgeon wisely. Extensive surgical experience can be helpful in achieving a good result and avoiding complications. Collectively, ROC orthopedic surgeons have performed more femur operations than any practice in Northern Nevada and take pride in outstanding surgical results.
In need of an orthopedic specialist? Schedule an appointment with one of our specialty-trained Fracture & Trauma doctors to talk through your options. Reno Orthopedic Clinic offers comprehensive treatment for a full range of traumatic injuries at multiple convenient locations in Reno, Sparks and Carson City.
